Natural Diabetes Management: How to Control Blood Sugar Without Medication
Natural ways to lower blood sugar
Best supplements for diabetes
Ayurvedic medicine for diabetes
Daily diet for diabetics
Diabetes control without medicine
How to reduce blood sugar levels quickly
Diabetes exercise for women
Sleep and diabetes connection
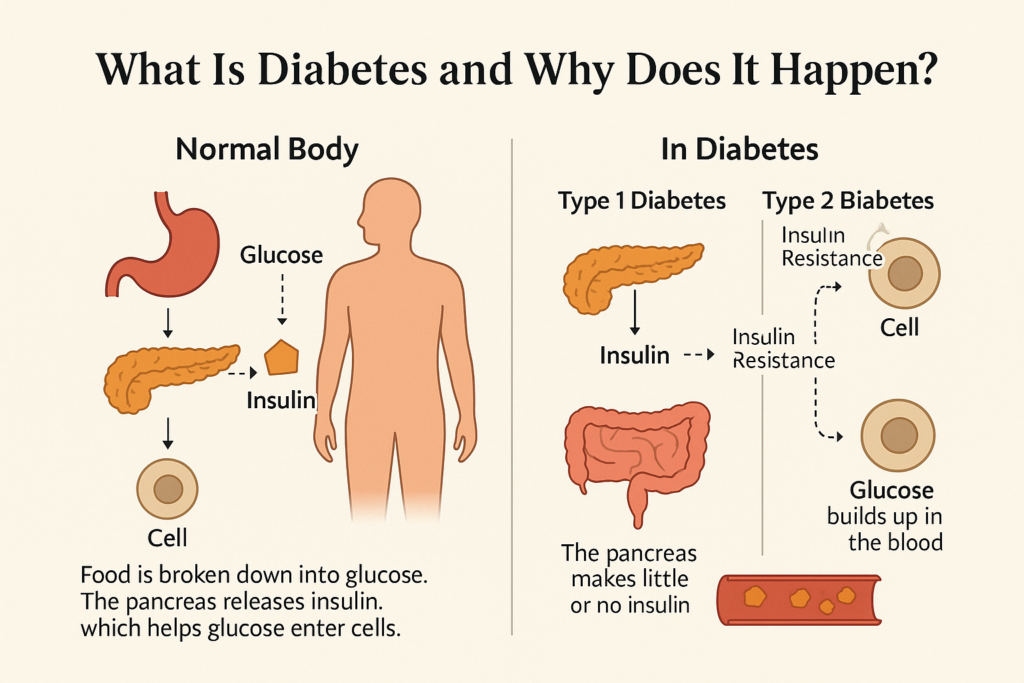
🔍 What Is Diabetes and Why Does It Happen?
Diabetes is a chronic condition where the body cannot properly process blood sugar due to insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production. The most common form is Type 2 diabetes, which is largely influenced by diet, activity levels, stress, and sleep.
Normal Body:
When you eat food, your body breaks it down into glucose (sugar). The pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps move glucose from your blood into your cells for energy.In Diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes – The pancreas produces little or no insulin.
Type 2 Diabetes – The body’s cells don’t respond properly to insulin (insulin resistance), and the pancreas can’t keep up.
Result: Glucose builds up in the blood, causing high blood sugar.
🧠 What Causes Type 2 Diabetes?
Excess sugar and refined carbs
Sedentary lifestyle
Chronic stress
Sleep deprivation
Obesity
Family history (but lifestyle is more impactful)
🔍 Know the Differences Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
| Feature | Type 1 Diabetes | Type 2 Diabetes |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Can happen at any age | More common in adults |
| Cause | Body stops producing insulin; can be inherited or genetic | Body cannot use insulin efficiently or does not make enough |
| Risk Factors | Genetic predisposition | Obesity, inactive lifestyle, and family history |
| Symptoms | Blurry vision, frequent urination, tiredness, unexplained weight loss | Same symptoms as Type 1 |
| Treatment | Insulin, diet, exercise, and blood glucose monitoring | Diet, exercise, medications, and insulin injections |
🌱 How to Control Diabetes Naturally (Without Medication)
🥗 1. Focus on a Blood Sugar-Friendly Diet
A diabetic-friendly diet is the foundation of reversing or controlling diabetes.
✅ Foods to Include:
Leafy greens, broccoli, berries
Whole grains like quinoa or oats
Healthy fats: avocados, olive oil, chia seeds
Protein: legumes, fish, eggs
❌ Foods to Avoid:
Sugary drinks and soda
White bread, pasta, pastries
Fried and processed foods
Daily diet for diabetics: Think fiber-rich, low-carb, high-protein meals.
2.💊 Best Supplements for Diabetes Management
If you’re looking for natural supplements to support blood sugar control, here are some clinically-backed options:
🟩 Berberine
Mimics insulin in the body and helps improve glucose uptake.
🟩 Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA)
A powerful antioxidant that supports nerve health and insulin sensitivity.
🟩 Ceylon Cinnamon
May help lower fasting blood sugar and reduce insulin resistance.
🟩 Magnesium
Magnesium deficiency is common in people with Type 2 diabetes, and it plays a vital role in regulating insulin.
✅ Recommended:
Doctor’s Best High Absorption Magnesium Glycinate Lysinate
100% chelated for better absorption
Vegan, non-GMO, gluten and soy-free
Gentle on the stomach
Provides 200 mg elemental magnesium per serving
This form is ideal for those seeking magnesium without digestive side effects, and its bioavailability makes it especially helpful for those managing insulin resistance.
🟩 Omega-7 (Sea Buckthorn)
Supports healthy lipid levels and reduces inflammation.
Choose GMP-certified brands. Always consult your doctor first.
🏃♀️ 3. Which Exercise is Best for Diabetes?
Exercise acts like natural insulin.
🚶 Best exercises for diabetes:
Brisk walking (30 mins a day)
Swimming
Cycling
Weight training (2–3x/week)
Yoga and Pilates (especially for women)
Even 10-minute walks after meals help lower blood sugar quickly.
🔄 How often should you exercise for diabetes?
At least 150 minutes per week, divided across 5 days.
🧘 4. Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Diabetes Control
Manage stress: Use breathing exercises, nature walks, or journaling
Improve sleep: 7–9 hours/night
Stay hydrated: Drink 2–3 liters of water per day
Sleep and diabetes: Poor sleep raises cortisol and blood sugar. Quality sleep is essential.
🌿 Ayurvedic Medicine for Diabetes
Ayurveda offers natural remedies that align with modern science.
🔹 Best Ayurvedic herbs for diabetes:
Gudmar (Gymnema) – Reduces sugar cravings
Karela (Bitter melon) – Improves sugar metabolism
Fenugreek (Methi) – Slows down sugar absorption
Turmeric (Curcumin) – Anti-inflammatory, improves insulin sensitivity
Available in capsule or powder form—great for busy Western lifestyles.
🌍 How Americans and Europeans Can Manage Diabetes Holistically
People in the U.S., UK, France, and Germany are shifting toward:
Lifestyle medicine
Digital tools (like CGMs and fitness trackers)
Functional and integrative health approaches
Combining supplements with dietary changes
Diabetes control without medicine is possible—with education, intention, and support.
🌞 Sample Daily Routine for Natural Diabetes Control
Morning:
Lemon water
30-minute walk or yoga
Oatmeal with chia seeds and berries
Afternoon:
Lunch: Quinoa salad, grilled tofu, olive oil
Herbal tea (like cinnamon or fenugreek)
Evening:
Dinner: Baked salmon, roasted vegetables
20-minute walk
Sleep by 10 PM
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
💡 What are the natural ways to lower blood sugar?
Eat a low-carb, high-fiber diet, exercise regularly, reduce stress, and use proven supplements like berberine and cinnamon.
💡 How to reduce blood sugar levels quickly?
Go for a 10-minute walk after eating, drink water, and avoid sugary foods immediately.
💡 What is the best exercise for diabetic women?
Yoga, brisk walking, Pilates, and resistance band workouts are great for women managing diabetes.
💡 Can sleep impact blood sugar?
Yes! Lack of sleep raises cortisol and makes your body more insulin resistant.
💡 What is the best Ayurvedic medicine for diabetes?
Gudmar, turmeric, fenugreek, and bitter melon are among the most effective herbs.
📌 Final Takeaway
Diabetes is manageable—and even reversible—with conscious changes. Whether you’re in New York, Paris, or Berlin, you can take charge of your health with:
✅ Balanced nutrition
✅ Simple movement routines
✅ Proven natural supplements
✅ Restorative sleep
✅ Ayurvedic wisdom
You don’t need to rely solely on pills. Your daily habits are the best medicine.
17 Natural Ways to Manage Blood Sugar Effectively
– A Real-Life Guide
Managing blood sugar isn’t about harsh rules—it’s about making smarter, doable choices every day. With the right food, habits, and mindset, you can feel more balanced, energetic, and in control. Here’s a detailed guide with practical food suggestions and supplement tips.
1. Move Your Body (Physical Activity)
Exercise helps your body use insulin more efficiently. It lowers blood sugar by moving glucose from your bloodstream into your cells.
What to do:
Walk for 30–45 minutes daily (brisk walking is best)
Add strength training 2–3 times a week (even bodyweight workouts work)
Light yoga or stretching on off-days helps with blood circulation
2. Control Your Carb Intake
Carbohydrates break down into glucose. Eating too many—especially refined ones—can spike your blood sugar.
Better choices:
Switch white rice with brown rice or quinoa
Choose whole wheat roti instead of white bread
Try chickpea pasta or lentil-based options for more fiber and protein
Supplement tip:
Pair carbs with protein (like eggs, Greek yogurt, or tofu) to slow sugar absorption.
3. Eat More Fiber
Fiber slows down the digestion of carbs, preventing sugar spikes and keeping you fuller longer.
High-fiber foods (with approx. fiber content):
Chia seeds: 10g per 2 tbsp
Lentils (masoor, moong): 15g per cup (cooked)
Oats: 4g per ½ cup
Avocado: 10g per medium fruit
Broccoli: 5g per cup (cooked)
Supplement options:
Psyllium husk (Isabgol): Start with 1 tsp in water before meals
Organic acacia fiber or inulin powder: Easily mixes with smoothies
4. Drink More Water
Water helps your kidneys flush out excess sugar and keeps you hydrated.
How much:
Aim for 2–3 liters per day (more if you’re active or live in a hot climate)
Add lemon, cucumber, or mint if you need flavor
5. Practice Portion Control
Eating large portions—even of healthy foods—can raise blood sugar.
Tips:
Use smaller plates
Fill half your plate with veggies, one-quarter with protein, and one-quarter with carbs
Avoid second helpings—wait 15 minutes first
6. Eat Low-Glycemic Foods
These foods digest slowly and prevent sugar spikes.
Top picks:
Sweet potatoes (boiled): GI ~44
Lentils and beans: GI ~30
Barley & quinoa: GI ~50
Apples and pears (with skin): GI ~38
Supplement idea:
Add cinnamon (Ceylon preferred) to smoothies or oatmeal—may help lower blood sugar.
7. Manage Stress
Stress hormones like cortisol can raise blood sugar, even without food.
Helpful techniques:
Deep breathing: Try 4-7-8 method
Journaling or talking to someone
Meditation (10 mins daily can make a big difference)
8. Improve Sleep Quality
Poor sleep messes with insulin sensitivity and sugar metabolism.
Tips for better sleep:
Stick to a sleep schedule (even on weekends)
Avoid screens 1 hour before bed
Magnesium supplements (200–400 mg) may support relaxation
9. Get Enough Chromium & Magnesium
Both minerals help insulin work better.
Good food sources:
Magnesium: Pumpkin seeds, spinach, almonds, dark chocolate (85%+ cocoa)
Chromium: Broccoli, oats, whole grains, and eggs
Supplements:
Magnesium glycinate (gentle on stomach)
Chromium picolinate (200 mcg/day is common dose)
10. Use Medicinal Foods
Some natural foods can support blood sugar balance.
Top options:
Fenugreek seeds (methi dana) – soak 1 tsp overnight, drink in morning
Bitter melon (karela) – cooked or in juice form
Cinnamon (Ceylon) – ½ tsp daily
Turmeric – anti-inflammatory and supports insulin sensitivity
11. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Even 5–7% weight loss can significantly improve blood sugar control.
Tip: Focus on body composition, not just the scale. Building muscle through strength training helps too.
12. Choose Healthy Snacks
Snacking smart prevents blood sugar crashes and overeating at meals.
Good options:
Handful of almonds or walnuts
Greek yogurt with chia seeds
Boiled eggs with cucumber
Roasted chickpeas
13. Add Probiotic Foods
Gut health is closely tied to how well your body handles sugar.
Food sources:
Yogurt with live cultures (check label)
Kefir
Sauerkraut or kimchi
Buttermilk (chaas)
Supplement tip:
Choose a multi-strain probiotic with at least 5–10 billion CFUs.
14. Watch Your Health When You're Sick
Illness, infections, or even a fever can raise blood sugar.
What to do:
Stay hydrated
Monitor sugar more frequently
Consult your doctor if your levels stay high despite medication
15. Be Mindful with Caffeine
Caffeine affects everyone differently. In some people, it can spike blood sugar or increase insulin resistance temporarily.
Best practices:
Limit to 1–2 cups of coffee or tea per day
Avoid sugary drinks like sweetened lattes or energy drinks
Try switching to herbal teas like chamomile or cinnamon if sensitive
Note: If you feel jittery or your sugar spikes after coffee, try skipping it for a few days and monitor the change.
16. Understand Your Insulin (If Applicable)
If you take insulin, knowing how it works with your meals, activity, and stress is key.
Tip:
Keep a log of blood sugar, meals, and insulin doses to identify patterns
Discuss with your doctor about insulin timing if you’re having frequent highs/lows
17. Know the Dawn Phenomenon
Some people experience high sugar in the early morning, even if they didn’t eat overnight.
Ways to manage it:
Eat a protein-rich dinner (e.g., grilled chicken with vegetables)
Avoid high-carb snacks at night
Talk to your doctor about adjusting insulin or meds if needed
Final Thought
Small, steady steps go a long way. The goal isn’t perfection—it’s progress. Listen to your body, eat mindfully, and don’t hesitate to get support. Your blood sugar doesn’t have to run your life—you’ve got this!